The Volumetric Velocimetry System equipment is being used to study surface-subsurface flow interactions in a physical model of a salmon redd at the University of Idaho, Center for Ecohydraulics Research. Female salmonids bury their eggs in streambed gravel by digging a pit where they lay their eggs, which they then cover with gravel from a second pit, forming a dune-like structure called a redd, which has coarse grains on the surface due to the winnowing away of fine material. The interaction between a redd and the stream flow induces surface water to enter the sediment, flow through the egg pockets, and reemerge downstream of the redd crest.
These downwelling and upwelling flows form the hyporheic exchange, which is vital for the embryos’ development because it regulates the egg pocket temperature regime and delivers oxygen-rich surface water to the embryos. Here, we experimentally investigate the effects of (1) redd surface roughness and (2) egg pocket presence on redd-induced hyporheic flows under different surface hydraulics. We use non-intrusive optical measurement techniques, including stereo particle image velocimetry (SPIV) and planar laser-induced fluorescence (PLIF), in a large-scale flume by matching the refractive index of the solid grains (made of THV) and the fluid (water mixed with 15% Epsom salt). This allows us to see through the solid matrix of grains and map the flow fields above and within the salmon redd.
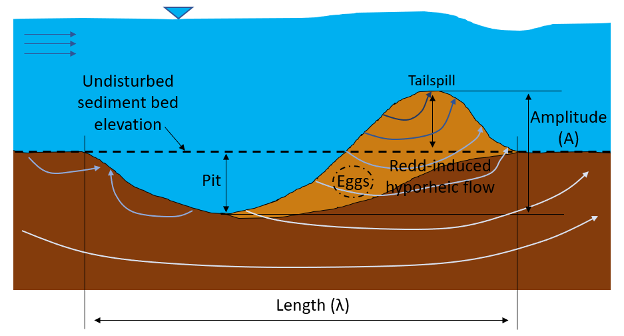

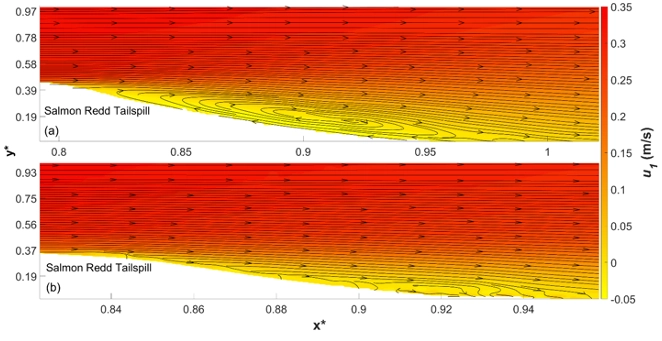
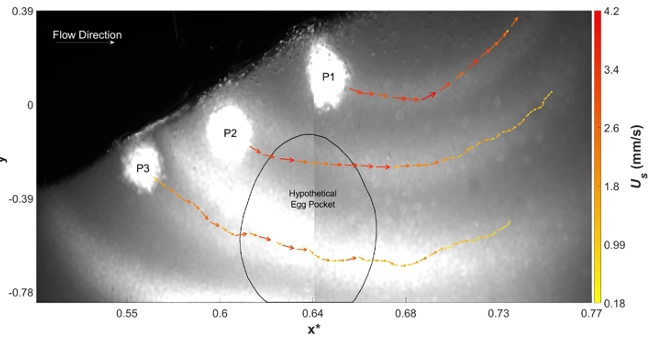
Subsurface flows into the smooth redd. The subsurface grain are homogeneous for this case (no artificial egg pocket).
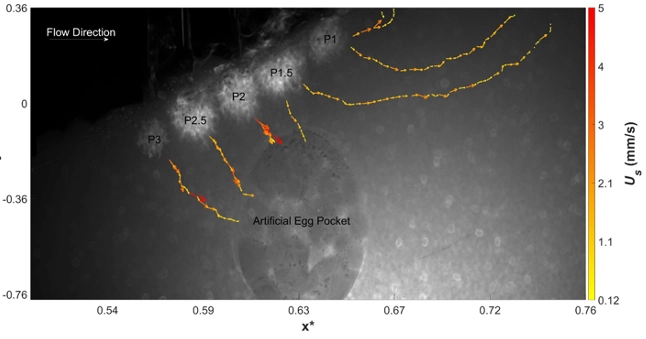
Subsurface flows into the rough redd. Note dispersion as flow passes through the artificial egg pocket.
Publications
Brandon Hilliard, William J Reeder, Ralph Budwig, Vibhav Dugesh, Bishal Bhattara, Benjamin T. Martin, Tao Xing & Daniele Tonina. Unveiling surface-subsurface flow interactions of a salmon redd. Manuscript in preparation (November 2023).
Bishal Bhattara,, Brandon Hilliard, William J Reeder, Ralph Budwig,, Benjamin T. Martin, Tao Xing, & Daniele Tonina. 2023. The Role of Riverine Bed Roughness, Egg Pocket Location, and Egg Pocket Permeability on Salmonid Redd-Induced Hyporheic Flows, Water Resources Research, doi: 10.1029/2023WR035548
Brandon Hilliard, Ralph Budwig, Richard S Skifton, Vibhav Durgesh, William J Reeder, Bishal Bhattara, Benjamin T. Martin,Tao Xing & Daniele Tonina. 2023. Measuring porous media velocity fields and grain bed architecture with a quantitative PLIF-based technique. Meas. Sci. Technol, 34, doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/acfb2b
Bishal Bhattara,, Brandon Hilliard, William J Reeder, Ralph Budwig,Benjamin T. Martin, Tao Xing, & Daniele Tonina. 2023. Effect of Surface Hydraulics and Salmon Redd Size on Redd-Induced Hyporheic Exchange, Water Resources Research, doi: 10.1029/2022WR033977
Brandon Hilliard, William J Reeder, Richard S Skifton, William Basham†, Ralph Budwig, & Daniele Tonina. 2021. A biologically friendly, low‐cost and scalable method to map permeable media architecture and interstitial flow. Geophysical Review Letters, 48(3), doi: 10.1029/2020GL090462
Tonina, D., Buffington, J.M., 2009a. A three-dimensional model for analyzing the effects of salmon redds on hyporheic exchange and egg pocket habitat. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 66, 2157–2173, doi: 10.1139/F09-146
